Introduction
CveGuardian is a sophisticated real-time CVE monitoring and management system designed to empower developers and security teams with comprehensive vulnerability tracking and mitigation capabilities. This powerful platform automatically scans software projects for dependencies, cross-referencing them against the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) to identify potential security risks. The system’s core functionality includes monitoring multiple repositories, analyzing which projects are affected by specific CVEs, and providing high-level visualizations of security risks through an intuitive web dashboard. The platform integrates seamlessly with DepScanity for advanced dependency analysis, offering developers robust filtering, search capabilities, and aggregated alerts that provide clear visibility into their application security posture.
System Architecture and Components
CveGuardian’s system architecture is built as a Bun monorepo with four interconnected components working in harmony to provide comprehensive CVE cross-referencing capabilities. The Web Application (apps/web) serves as the user-facing interface, delivering a React-based dashboard powered by TypeScript and Vite for rapid development and hot module replacement. This frontend features ESLint integration, Tailwind CSS styling, and provides intuitive visualization of security data and alerts. The API Server (apps/api) operates as the central orchestrator, utilizing Hono framework to handle business logic, manage repository cloning and DepScanity execution for dependency scanning, and deliver full CRUD operations for project management. It aggregates statistics, powers advanced filtering and search capabilities for CVEs and impacted projects, and leverages Drizzle ORM for robust database operations. The Fetcher Service (apps/fetcher) functions as a background worker that synchronizes CVE data from the National Vulnerability Database through scheduled cron jobs, ensuring the local vulnerability database remains current with new and modified entries. The Core Library (packages/core) serves as the shared foundation across all workspaces, containing essential Drizzle ORM schema definitions and singleton database connection logic while providing common types and utilities that maintain consistency throughout the entire system architecture.
How CveGuardian Monitors Vulnerabilities
CveGuardian employs a comprehensive vulnerability monitoring workflow that seamlessly integrates multiple components to provide robust security coverage across distributed repositories. The process begins with NVD Synchronization, where the Fetcher service executes scheduled cron jobs to pull fresh CVE data from the National Vulnerability Database, maintaining an up-to-date local database of threat intelligence. This foundational step ensures access to authoritative vulnerability information. Following this, the API server orchestrates Dependency Scanning by cloning registered repositories and executing DepScanity—an external analysis tool that must be manually compiled and positioned in the tools/DepScanity/ directory—allowing for thorough examination of project dependencies to identify vulnerable packages. The system then performs Impact Analysis by cross-referencing discovered dependencies against the synchronized CVE database, pinpointing specific vulnerabilities affecting particular projects and assessing severity levels. Finally, Real-time Monitoring maintains continuous security posture through scheduled background jobs that refresh vulnerability data and provide users with dashboard visibility into affected projects, creating a complete automated workflow that requires minimal manual intervention while delivering comprehensive security insights across multiple repositories.
Key Features for Security Teams
CveGuardian offers comprehensive security capabilities designed to streamline vulnerability management for both security teams and developers. Its React-based dashboard provides intuitive visualization of security postures, displaying real-time statistics, critical alerts, and aggregated risk metrics that offer immediate visibility into compromised projects. The platform’s robust project management system enables full CRUD operations, allowing teams to monitor multiple repositories from a centralized interface while organizing projects by team or priority and managing scanning schedules effectively. Advanced CVE filtering and search functionality empowers users to conduct precise vulnerability research across the entire CVE database, with options to filter by severity levels, date ranges, affected products, and CVSS scores. The system’s core cross-referencing capability maps vulnerabilities directly to project dependencies, identifying specific impacted projects and showing dependency chains that reveal transitive vulnerabilities. This feature addresses the critical question of actual exposure rather than theoretical risk, enabling intelligent prioritization of security efforts. Additional capabilities include automated scanning that eliminates manual tracking, aggregated alerts for proactive monitoring, and comprehensive statistics that support security reporting and trend analysis.
Getting Started with CveGuardian
Getting Started with CveGuardian requires careful attention to its dependency structure and configuration setup. The critical prerequisite is DepScanity, which must be obtained separately from its GitHub repository at https://github.com/ettoremessina/DepScanity, compiled according to its documentation, and placed in the tools/DepScanity/ directory within the CveGuardian project. Once DepScanity is properly configured, clone the CveGuardian repository from GitHub and ensure Bun package manager is installed, as it serves as the foundation for managing monorepo workspaces. Execute bun install to install all necessary dependencies for the complete system operation. Configuration involves copying the example environment file with cp .env.example .env and editing it to include essential secrets such as Database URL, API keys for external services, WordPress credentials for integration, and NVD API configuration. To run the system effectively, begin by starting the Fetcher service to synchronize CVE data from NVD, followed by launching the API server and Web application for dashboard access. Initial setup tasks include configuring project repositories for monitoring, triggering dependency scans, reviewing security posture through the dashboard, and establishing alert preferences. Proper environment configuration is crucial for database connectivity and API access, while the initial NVD synchronization may require considerable time depending on data volume and system performance.
CveGuardian User Interface
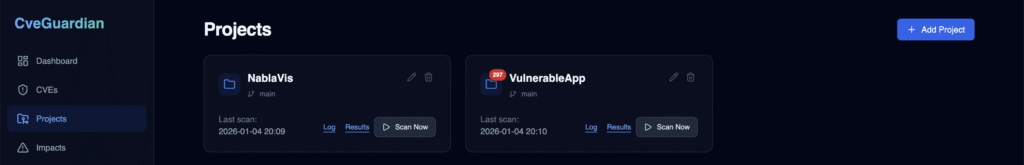
Navigate CveGuardian through four main sections in the left menu: Dashboard (security overview), Projects (repository tracking), CVEs (vulnerability database), and Impacts (cross-referencing vulnerabilities with your projects).
Dashboard feature is at-a-glance summary:
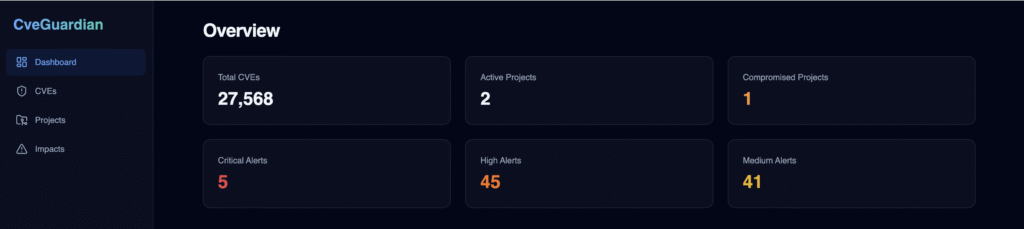
CVEs feature allows the user to browse and search the complete CVE database with powerful filtering capabilities. Filter by CVE code and description, date and severity quickly.
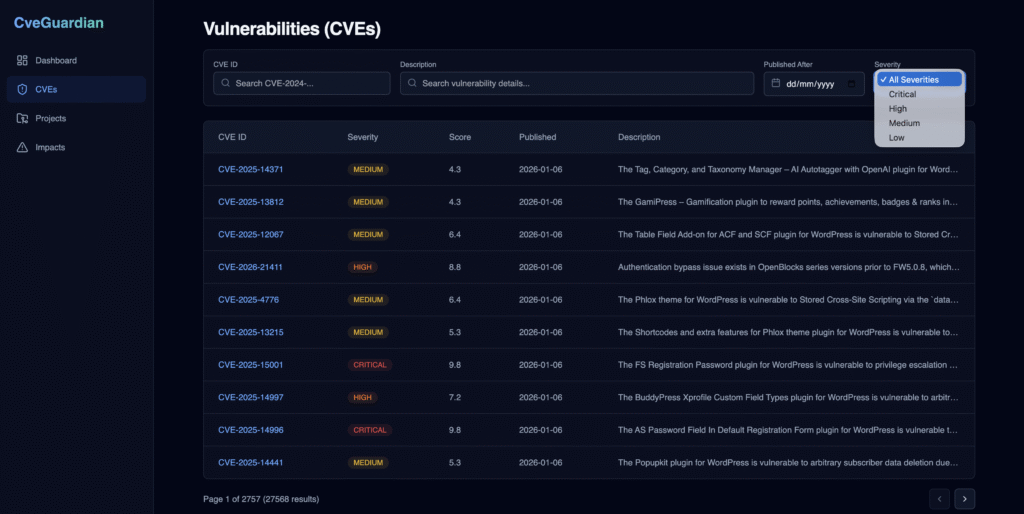
The Projects feature is a centralized repository management for vulnerability tracking. Register new projects, run scan to get vulnerable dependencies, view vulnerable project dependencies, monitor scan log and scan results:
Impacts feature answers the critical question: which projects are affected by this CVE? User can view direct and transitive dependency relationships, identify exposed repositories, and assess real-world impact for informed security decisions.
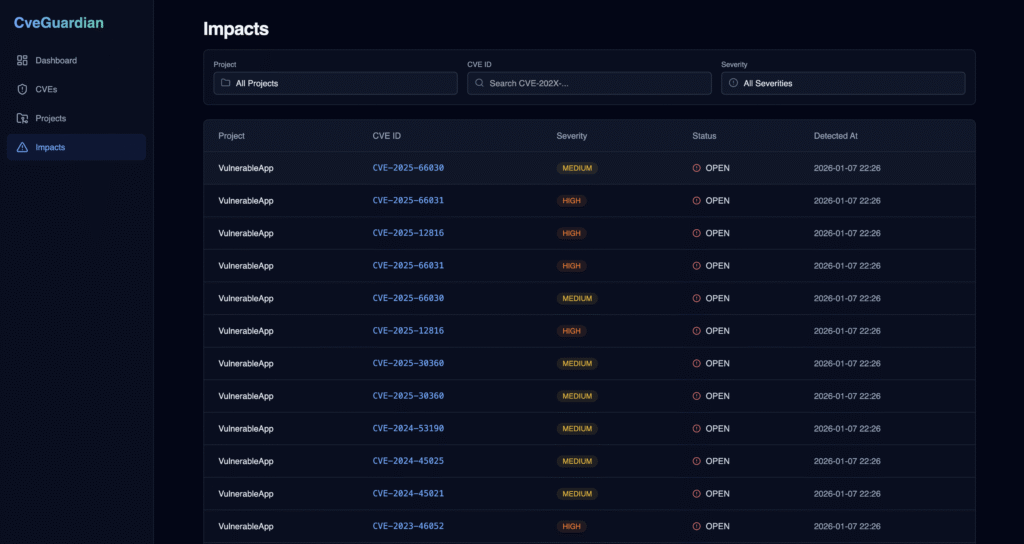
Because knowing which projects are vulnerable matters.
Download of the Complete Code
The complete code is available at GitHub. This program is written using Gemini3 code agent inside the Antigravity IDE.
These materials are distributed under MIT license; feel free to use, share, fork and adapt these materials as you see fit.
Also please feel free to submit pull-requests and bug-reports to this GitHub repository or contact me on my social media channels available on the contact page.
FAQ
What does CveGuardian do and how does it help software security teams?
CveGuardian is a comprehensive monitoring and management system designed to track vulnerabilities in software projects by cross-referencing CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) with project dependencies. It helps security teams by automatically identifying and analyzing security risks in their software supply chains, providing centralized visibility into known vulnerabilities across all project components. The system monitors for new CVEs, correlates them with specific dependencies in projects, and provides actionable insights to help teams prioritize and remediate security issues effectively.
Can you explain the system architecture of CveGuardian?
CveGuardian follows a Bun monorepo architecture with distinct components working together. The system includes Web (frontend interface), API (backend services), Fetcher (vulnerability data collection), and Core (business logic layer). The Web component provides the user interface, API handles service requests and data operations, Fetcher synchronizes vulnerability data from sources like NVD, and Core manages the core logic for vulnerability correlation and analysis. This modular architecture enables efficient development, testing, and deployment of security monitoring capabilities.
How does vulnerability monitoring work in CveGuardian?
CveGuardian’s vulnerability monitoring operates through multiple mechanisms including NVD (National Vulnerability Database) synchronization, DepScanity integration for dependency analysis, and continuous scanning of project dependencies. The system automatically fetches updated vulnerability data from NVD feeds, scans projects for vulnerable components using DepScanity integration, and performs impact analysis to determine the severity and scope of identified vulnerabilities. It continuously monitors for new CVEs and updates its database to ensure real-time vulnerability awareness.
What are the key features of CveGuardian’s dashboard and project management capabilities?
CveGuardian provides comprehensive dashboard visualization showing security metrics, vulnerability trends, and project health status. Key features include project management tools for organizing and tracking multiple software projects, advanced CVE filtering capabilities to prioritize threats based on severity or impact, and robust cross-referencing functionality that connects CVEs directly to specific project dependencies. The system also offers customizable alerts, historical vulnerability tracking, and detailed impact analysis reports that help security teams make informed remediation decisions.
What technology stack does CveGuardian use for its frontend and backend?
CveGuardian uses a modern technology stack built on React with TypeScript and Vite for the frontend, providing fast development and excellent type safety. For backend services, it leverages the Hono framework for lightweight API handling, Drizzle ORM for database operations with excellent TypeScript integration, and Bun as the runtime environment. This combination delivers high performance, type safety, and efficient development workflows while maintaining compatibility with modern JavaScript ecosystems.
Why does CveGuardian require DepScanity and how do I obtain it?
CveGuardian requires DepScanity as a critical dependency for accurate project dependency analysis and vulnerability correlation. DepScanity provides the capability to parse and analyze software dependencies across multiple package managers and programming languages, which is essential for CveGuardian’s cross-referencing functionality. To obtain and install DepScanity, you need to download it from the official repository or package manager, ensure it’s properly configured in your environment, and follow the installation instructions specific to your operating system and development setup.
What is the complete installation and setup process for CveGuardian?
The installation process involves cloning the repository, installing dependencies using Bun, setting up environment configuration with .env files containing database credentials and API keys, configuring the database schema using Drizzle ORM, and installing the required DepScanity dependency. You’ll need to run database migrations, configure API keys for NVD access and other services, set up the appropriate package manager support, and ensure all necessary environment variables are properly defined. The system also requires proper file permissions and network access for external data synchronization.
How do I configure the environment and database settings for CveGuardian?
Environment configuration requires creating a .env file with essential parameters including DATABASE_URL for database connection, NVD_API_KEY for accessing vulnerability feeds, and various service credentials. Database setup involves configuring the database connection string with appropriate authentication details, ensuring proper schema migrations are applied using Drizzle ORM, and setting up the database user with necessary permissions. You’ll also need to configure API keys for external services, define project-specific settings, and establish proper security configurations for database access.
How do I run and access CveGuardian once it’s installed?
To run CveGuardian, you need to start the Bun development server or build the production environment, then launch the API services and frontend components. Access the dashboard through your configured web browser at the specified port (typically localhost:3000 or custom port). The system provides a user-friendly interface where you can view security dashboards, manage projects, configure monitoring settings, and access detailed vulnerability reports. Background services automatically sync vulnerability data and scan project dependencies according to configured schedules.
What are the primary use cases for CveGuardian in security operations?
CveGuardian serves several critical use cases for security teams including continuous monitoring of software supply chains, automated vulnerability detection in development environments, compliance reporting for regulatory requirements, and proactive security management across multiple projects. It’s particularly valuable for DevOps teams integrating security into CI/CD pipelines, security operations centers monitoring enterprise applications, and development teams tracking vulnerabilities in their dependencies. The system supports incident response workflows, security audit preparation, and provides detailed analytics for security governance initiatives across organizations.



